Competencies, Supports and Enablers for Engagement Capable Ontario Health Teams
This framework outlines the competencies, supports and enablers needed to build engagement-capable OHTs. Competencies are the essential knowledge, skills, attitudes and beliefs that are necessary to be successful within a certain field, in this case, for patient, family and caregiver engagement and partnering. Supports and enablers provide the infrastructure that fosters the competency development required to build and sustain engagement-capable OHTs.
The downloadable framework document includes the sections and supporting resources outlined below:
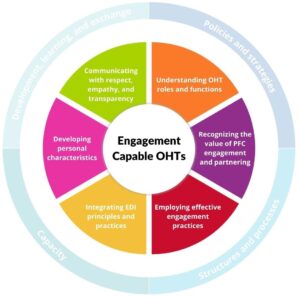
Competency Domains
Six competency domains outline the key competencies required for OHT staff, leadership and PFC partners to successfully work together to create engagement-capable OHTs. Each of these domains includes sub-domains and resources. The domains include:
1. Understanding OHT roles and functions in relation to health and social services systems
2. Recognizing the value of PFC engagement and partnering
3. Employing effective PFC partnership and engagement practices
4. Integrating Equity, Diversity and Inclusion (EDI) principles and practices into all engagement and partnering work
5. Developing personal characteristics to enhance meaningful and authentic engagement
6. Communicating with respect, empathy, and transparency
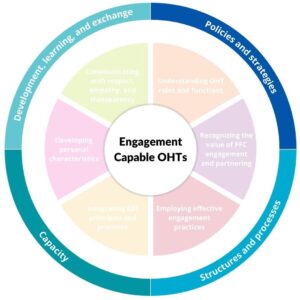
Support and Enabler Domains
Four support and enabler domains provide the infrastructure that OHT leadership, staff and PFC partners need to work together in an environment that fosters respectful and effective engagement. Not all of these are under the direct control of OHTs and need to be developed in partnership with others (e.g., Ministry of Health, Ontario Health). Each of these domains includes sub-domains and resources. The domains include:
1. Policy and strategies
2. Structures and processes
3. Capacity
4. Development, learning and exchange
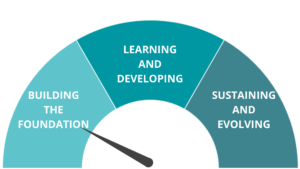
Patient, Family and Caregiver Engagement and Partnering in OHTs: A Path to Maturity
Acknowledging that building an engagement-capable culture takes time, this path to maturity outlines the key expectations of OHTs at three stages:
- Building the foundation
- Learning and developing
- Sustaining and evolving
About this Framework
This framework was developed by a working group of Patient, Family and Caregiver (PFC) partners, Ontario Health Team (OHT) leadership and staff, and Ministry representatives, co-chaired by Julia Abelson (Public and Patient Engagement Collaborative) and Betty-Lou Kristy (Minister’s Patient and Family Advisory Council) which met between December 2022 and March 2023.
We are grateful to the over one hundred PFC partners, OHT leaders, providers, engagement staff and equity specialists across the province who contributed to the framework’s development at various stages through surveys, group and one-on-one consultations.
We acknowledge the important work of Healthcare Excellence Canada in this area and their Engagement Capable Environments tool as well as early conceptual thinking about engagement capable environments1,2 which informed our work and helped us to further operationalize these important ideas.
1Baker, G.R., Judd, M., Fancott, C., & Maika, C. (2016). Creating “engagement capable environments” in healthcare. In G.R. Baker, M. Judd, & C. Maika (Eds.), Patient engagement: Catalyzing improvement and innovation in healthcare (pp. 11 – 34). Longwoods Publishing Corporation. https://www.longwoods.com/content/24908/books+/creating-engagement-capable-environments-in-healthcare
2Baker, G.R., & Denis, J.-L. (2011). Patient engagement and system transformation – Patient engagement workshop. Edmonton, AB.
The Framework is currently available for download from our website in English and French
Working Group members include:
Julia Abelson, Professor, Public and Patient Engagement Collaborative, McMaster University (Working Group Co-Chair)
Betty-Lou Kristy, Chair, Minister’s Patient and Family Advisory Council, Ministry of Health (Working Group Co-Chair)
Reham Abdelhalim, Population Health Management and Evaluation Lead, Burlington Ontario Health Team
Lotje Hives, Patient Family Caregiver Council Representative and Collaboration Council Tri-chair, Nipissing Wellness OHT
Vyshnave Jeyabalan, North Toronto Ontario Health Team
Michelle MacKinnon, Senior Program Consultant, Patient Engagement Secretariat, Ministry of Health
Aleksandra Milosevic, Engagement Specialist, Ottawa Health Team-Équipe Santé Ottawa
Jessica Riehm, Manager, OHT Integrated Supports Unit, Ministry of Health
Maureen Smith, Patient Partner
Laura Tenhagen, Project Management Consultant, Sault Area Hospital
Lindsay Wingham-Smith, Executive Director, Mississauga Ontario Health Team
Laura Tripp, Research Coordinator, Public and Patient Engagement Collaborative, McMaster University
Andrea Dafel, Research Assistant, Public and Patient Engagement Collaborative, McMaster University
Rana Saleh, Research Assistant, Public and Patient Engagement Collaborative, McMaster University
Moizza Ul Haq, Research Assistant, Public and Patient Engagement Collaborative, McMaster University
